
Of those, a small number are running applications that manage the cluster. When you deploy Kubernetes, you get a cluster.Ī Kubernetes cluster consists of a set of nodes, which all run containerized applications. 6.2.3.5 Horizontal Pod Autoscaler Controller.6.2.3 Controller Manager kube-controller-manager.This also makes adding and removing compute nodes as needed easier, without needing to worry about core services being affected by a node being evacuated.

These dedicated nodes may have additional redundancy, different CPU/RAM requirements, and other low-level differences from compute nodes. registry, overlay network routing, and others to be hosted on dedicated nodes. This architecture enables the services which are critical to the cluster, i.e. This ensures that the services have resources available and are able to migrate in the event of host maintenance or failure. Red Hat recommends a minimum of three infrastructure nodes for production deployments. These nodes host cluster services such as log aggregation, metrics collection and reporting, container registry services, and overlay network management and routing. In addition to the architectures referenced above, Red Hat’s OpenShift introduces the concept of infrastructure nodes. Red Hat OpenShift infrastructure architecture ¶ This makes it very easy to burst, and reclaim, resources based on real-time application workload.Ĥ.2.4. Compute nodes can be added and removed from the cluster as needed quickly and easily to accommodate the scale of the applications which are being hosted. However, extra resources must be built into the compute infrastructure to accomodate any workloads from failed nodes. The master nodes are the control plane for the cluster and consequentially there should be special consideration given to their sizing and quantity.Ĭompute nodes are, generally speaking, much more disposable. If no masters are running, or the master nodes are unable to reach a quorum, then the cluster is unable to schedule and execute applications. Master nodes are critical to the operation of the cluster. Trident is installed the same no matter which kubernetes architecture is chosen. These accommodate various methods of high availablility and recoverability of the cluster, it’s services, and the applications running. There are three primary Kubernetes cluster architectures.
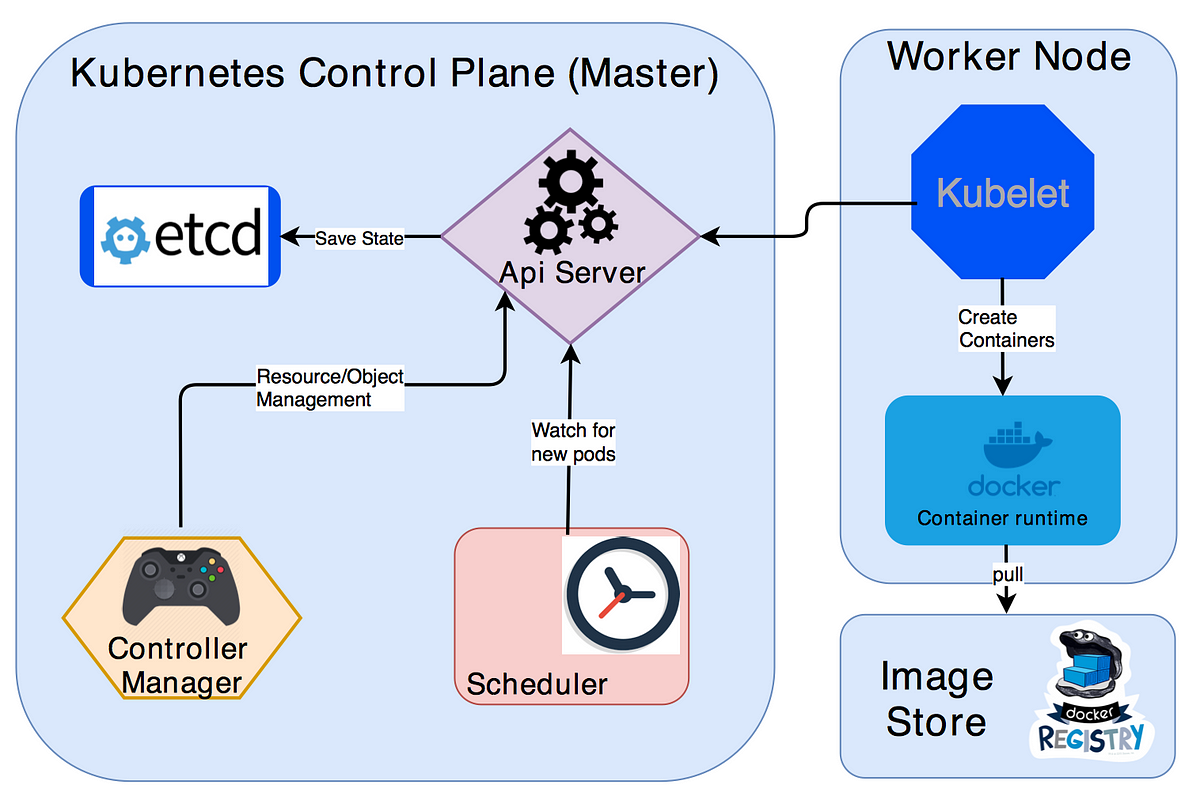
Some of these services, such as etcd and DNS, are mandatory for the cluster to be functional, while other services are optional. Depending on the service type, each service is deployed on only one type of node (master or compute) or on a mixture of node types. The cluster has a number of Kubernetes intrinsic services which are deployed in the cluster.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
